Bayesian Test Results Calculator 📊
An interactive web-based tool designed to help understand the often counter-intuitive results of diagnostic tests using Bayes' Theorem. This calculator visually and textually demonstrates how the base rate (prevalence) of a condition significantly impacts the true probability of having that condition given a positive test result. It serves as an educational resource to combat the base rate fallacy and provide a clearer understanding of conditional probability in real-life scenarios.
Demo
Live Demo 👈 Click here to try it out!
Features
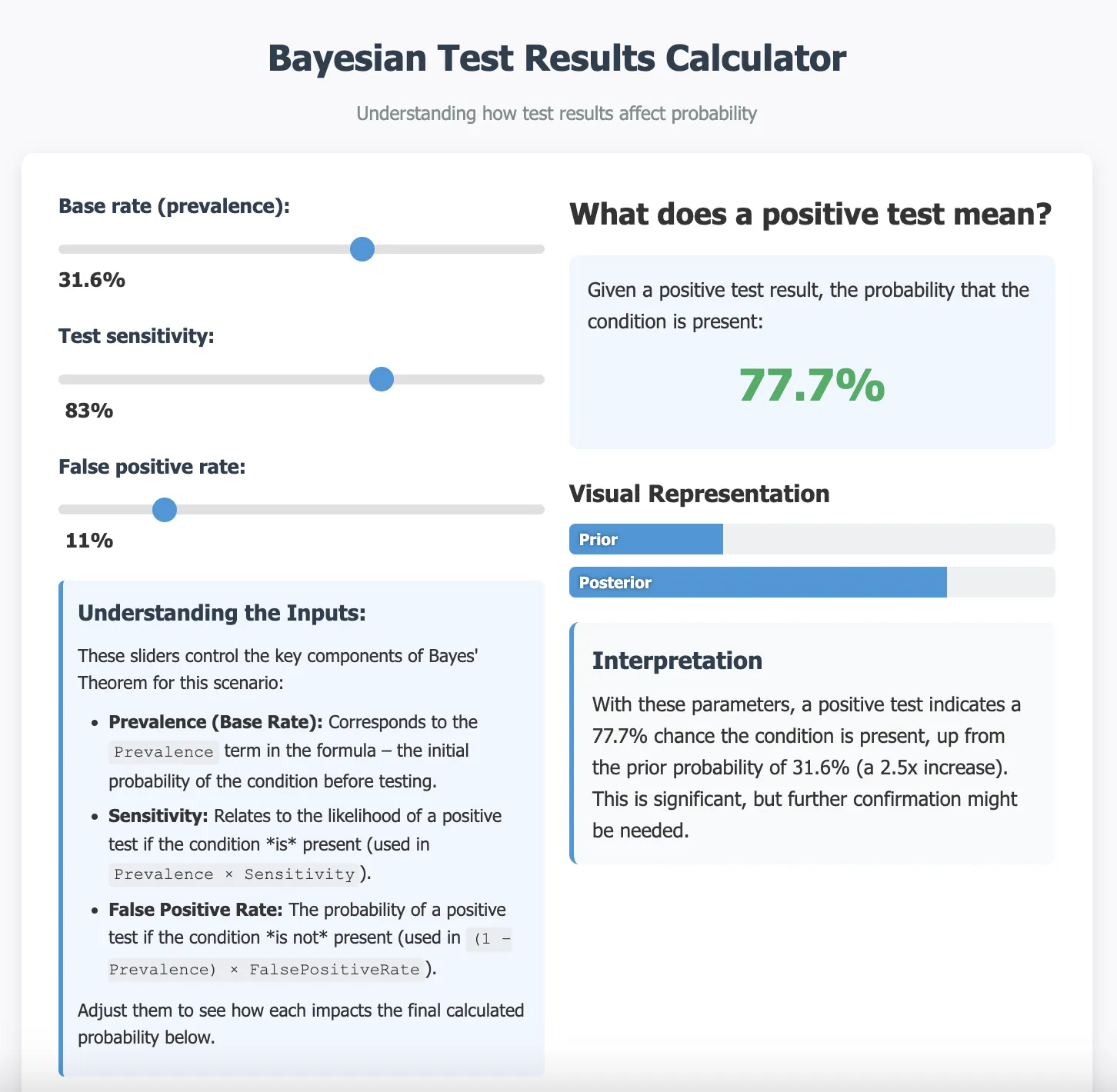
- Interactive Sliders: Adjust the Prevalence (Base Rate), Test Sensitivity, and False Positive Rate.
- Visual Representation: Compare the Prior Probability (Prevalence) and the Posterior Probability side-by-side with dynamic bar charts.
- Dark Mode: Toggle between light and dark themes for comfortable viewing.
How It Works
This calculator applies Bayes' Theorem to a common diagnostic testing scenario. The core formula implemented is:
P(Condition | Positive) = [Sensitivity * Prevalence] / [(Sensitivity * Prevalence) + (False Positive Rate * (1 - Prevalence))]
Where:
- P(Condition | Positive): The probability you actually have the condition given a positive test result (This is what the calculator outputs).
- Sensitivity: The probability of a positive test if you have the condition (
P(Positive | Condition)). - Prevalence: The overall probability of having the condition in the population before testing (
P(Condition)). - False Positive Rate: The probability of a positive test if you do not have the condition (
P(Positive | No Condition)). - (1 - Prevalence): The probability of not having the condition (
P(No Condition)).
The user adjusts the Prevalence, Sensitivity, and False Positive Rate using sliders, and the calculator computes and displays P(Condition | Positive) along with interpretations and visualizations.
Usage
- Open the Calculator: Access the [Live Demo] or open the
index.htmlfile locally. - Adjust Inputs: Use the sliders to set:
- The Base rate (prevalence) of the condition you're considering.
- The Test sensitivity (true positive rate) of the diagnostic test.
- The False positive rate of the test.
- Observe Results:
- The main Probability Result updates instantly.
- The Interpretation text explains the result in context.
- The Visual Representation bars change to reflect the prior vs. posterior probability.
- Learn More:
- Review the Parameter Summary in the input section to connect the sliders to the formula.
- Read the How It Works section for the formula breakdown.
- Explore the Key Insights for common takeaways.
- Check the Historical Context for background on Bayes' Theorem.
- Toggle Dark Mode: Use the switch in the top-right corner for your preferred theme.
Technologies Used
- HTML5: Semantic structure.
- CSS3: Styling, layout (Flexbox), responsiveness (Media Queries), and dark mode implementation.
- Vanilla JavaScript:
Potential Future Enhancements
- Option to input Test Specificity (1 - False Positive Rate) instead of FPR.
- Display intermediate calculation steps (numerator/denominator values).
- Add a glossary defining key terms (Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity, Posterior, etc.).
- Include alternative visualizations like natural frequency trees.
Historical Context & Acknowledgements
This tool demonstrates a concept formalized by Thomas Bayes (1701-1761), posthumously published by Richard Price (1763), and independently developed and popularized by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1774). Bayes' Theorem is a cornerstone of probability theory and finds critical applications in statistics, science, machine learning, medicine, and countless other fields.
License
Distributed under the GNU Affero General Public License v3.0 License. See LICENSE for more information.